Table of Contents

To select the right industrial neodymium magnet, you need to match strength, size, shape, grade, and coating to your operational needs. Application environment, temperature, and cost all play a major role in performance. The chart below shows how neodymium magnets offer high coercivity and strong magnetic force compared to other materials.
When you focus on both technical and practical factors, you ensure industrial neodymium magnets deliver reliable results in your application.
Key Takeaways
Start by defining the load and force your magnet needs to handle, adding a safety margin for reliability.
Measure the available space carefully and choose a magnet size and shape that fits without interfering with other parts.
Select a magnet grade that matches both the strength and temperature requirements of your application.
Consider the environment and use protective coatings like nickel or epoxy to prevent corrosion and damage.
Handle magnets with care using gloves and eye protection, and store them safely away from electronics and children.
Always test magnets in real-world conditions through prototyping to avoid costly mistakes.
Work with expert suppliers who can guide you on the right magnet choice and ensure quality and safety standards.
Balance your budget by choosing magnets that meet your needs without overspending, focusing on long-term value.
Application Needs
Load and Force
You need to start by defining the load and force requirements for your application. Every industrial task demands a specific holding or lifting strength. Calculate the maximum weight or force the magnet must handle. Use a safety margin to ensure reliability. For example, if you need to lift a 10-pound object, select a magnet rated for at least 12-15 pounds.
Tip: Always test the magnet in real-world conditions. Surfaces, air gaps, and materials can reduce the actual holding force.
You can use the following table to estimate the required pull force:
Application Type | Typical Load (lbs) | Recommended Safety Factor |
|---|---|---|
Light Holding | 1-5 | 2x |
Medium Lifting | 5-20 | 1.5x |
Heavy Industrial Use | 20+ | 1.2x |
Matching the magnet’s strength to your operational needs prevents accidents and equipment failure.
Space and Size
Measure the available space for the magnet in your setup. The size of the magnet must fit within your design without interfering with other components. Larger magnets provide more strength, but they may not always fit. Small magnets can work if you use high-grade or multiple units.
Check the length, width, and height of the installation area.
Consider the thickness of the magnet, as it affects both strength and fit.
Plan for any movement or vibration that could shift the magnet out of place.
Note: The shape and size of industrial neodymium magnets influence the magnetic field and how the force distributes across surfaces.
Choose a magnet that balances strength and size for the best performance.
Temperature
Temperature plays a critical role in magnet performance. Industrial neodymium magnets lose strength when exposed to high heat. Each magnet grade has a maximum operating temperature. Exceeding this limit can cause permanent loss of magnetism.
Identify the highest and lowest temperatures in your application.
Select a magnet grade that matches or exceeds these temperatures.
For environments above 80°C (176°F), consider high-temperature grades like N42SH or N48H.
Alert: Sudden temperature changes can also affect magnet stability. Always check the manufacturer’s specifications for temperature ratings.
By understanding your temperature needs, you prevent magnet failure and ensure long-term reliability.
Environment
You must consider the environment where you plan to use your magnets. Environmental factors can affect the performance and lifespan of industrial neodymium magnets. Moisture, humidity, and exposure to chemicals can cause corrosion. Dust and debris may also interfere with the magnetic field.
Check if your application involves outdoor use or exposure to water.
Identify any chemicals or solvents present in the area.
Look for temperature fluctuations or rapid changes in humidity.
Tip: Choose magnets with protective coatings if you expect harsh conditions. Nickel, epoxy, or gold coatings help prevent rust and damage.
If you ignore environmental factors, you risk magnet failure or reduced strength. Always match the magnet’s protection level to the demands of your workplace.
Safety
Safety should always come first when working with strong magnets. Industrial neodymium magnets can pinch fingers or damage equipment if handled carelessly. You need to plan for safe installation, handling, and removal.
Wear gloves and eye protection when handling large or powerful magnets.
Keep magnets away from electronic devices and magnetic storage media.
Store magnets in a secure place to prevent accidental injuries.
Alert: Magnets can snap together with great force. Keep them away from children and untrained staff.
You should also check for any regulations or safety standards that apply to your industry. Following safety guidelines protects both people and equipment.
Budget
Budget plays a key role in your selection process. You want to balance cost with performance and durability. Higher-grade magnets often cost more but provide better strength and temperature resistance. Coatings and custom shapes may also increase the price.
Set a clear budget before you start shopping.
Compare prices from different suppliers.
Consider the total cost, including installation and maintenance.
Note: Buying the cheapest option may lead to higher costs later if the magnet fails or wears out quickly.
You make the best investment when you choose magnets that meet your needs without overspending. Always factor in the long-term value, not just the upfront price.
Industrial Neodymium Magnets: Grades
Grade Basics
When you choose industrial neodymium magnets, you will see grades like N35, N42, or N52. The number after the “N” stands for the magnet’s maximum energy product (BHmax). This number tells you how strong the magnet is. Higher numbers mean stronger magnets. For example, N52 is much stronger than N35.
You may also notice letter codes after the number, such as M, H, SH, UH, or EH. These letters show how much heat the magnet can handle before it starts to lose strength. Each letter stands for a different temperature rating.
Tip: Always check both the number and the letter when you select a magnet. The number gives you strength, and the letter gives you temperature resistance.
Here is a quick guide to what these grades mean:
N35-N52: Standard grades, best for room temperature uses.
M (Medium): Up to 100°C, good for appliances and sensors.
H (High): Up to 120°C, used in motors and oil equipment.
SH (Super High): Up to 150°C, found in aerospace and turbochargers.
UH (Ultra High): Up to 180°C, used in electric vehicles and advanced machines.
EH (Extreme High): Up to 200°C, chosen for defense and advanced aerospace.
Strength Selection
You need to match the magnet’s strength to your application. The higher the grade, the stronger the magnetic field and pull force. For the same size, an N52 magnet will hold more weight than an N35 magnet. This difference can make a big impact on your project.
Here is a table that shows how strength changes with grade for a common magnet size:
Magnet Grade | Size (mm) | Surface Field Strength (Gauss) | Pull Force (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
N35 | 10 x 3 | 11,700 | 1.5 |
N42 | 10 x 3 | 12,800 | 2.0 |
N48 | 10 x 3 | 13,600 | 2.5 |
N52 | 10 x 3 | 14,500 | 3.0 |
N35 | 20 x 3 | 11,700 | 3.6 |
N42 | 20 x 3 | 12,800 | 4.5 |
N48 | 20 x 3 | 13,600 | 5.5 |
N52 | 20 x 3 | 14,500 | 6.0 |
You can see that as the grade increases, both the surface field strength and pull force go up. This means you can use a smaller, higher-grade magnet to get the same strength as a larger, lower-grade one.
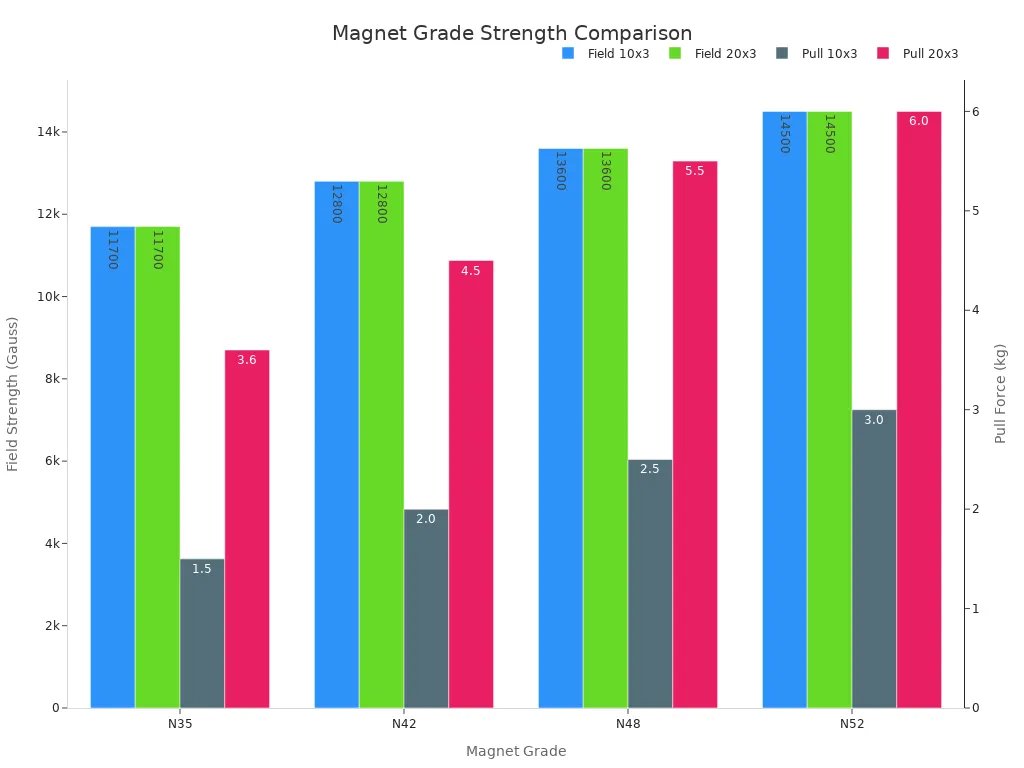
Note: Higher strength magnets usually cost more. You should balance the need for strength with your budget and safety requirements.
Temperature Ratings
Temperature can change how well industrial neodymium magnets work. If you use a magnet in a hot place, it may lose strength or even become useless. The letter codes after the grade number tell you how much heat the magnet can handle.
Here is a table that explains these codes:
Letter Code | Max Operating Temperature (°C) | Description |
|---|---|---|
None | 80 | Standard neodymium magnet |
M | 100 | Moderate temperature resistance |
H | 120 | High-temperature resistant |
SH | 150 | Super-high temperature resistant |
UH | 180 | Ultra-high temperature resistant |
EH | 200 | Extremely high temperature resistant |
TH | 230 | Top-level temperature resistance |
If your application gets hot, you need a magnet with a higher temperature rating. For example, a magnet with an “SH” code can work up to 150°C. If you use a standard grade magnet in a hot place, it may lose its magnetism.
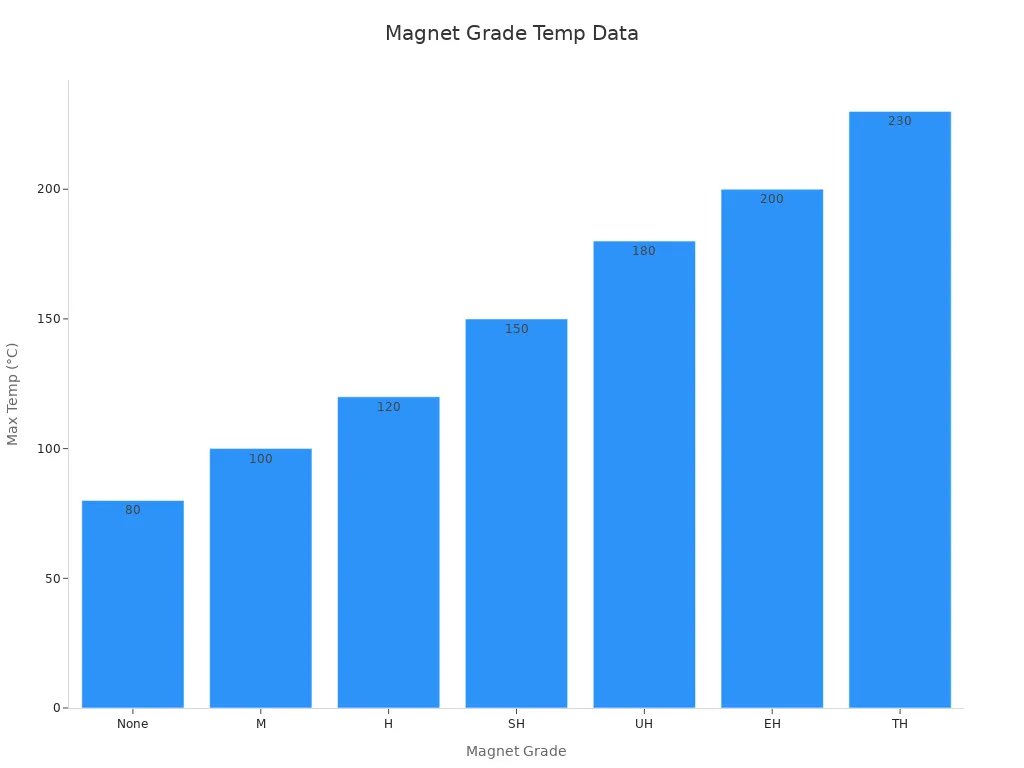
Alert: Sometimes, a lower strength magnet with a higher temperature rating costs more than a stronger magnet with a lower temperature rating. Always choose the grade that matches your real-world needs.
When you select industrial neodymium magnets, you must consider both strength and temperature. The right grade will help your equipment run safely and last longer.
industrial neodymium magnets Size and Shape
Common Shapes
You will find industrial neodymium magnets in many shapes. Each shape creates a different magnetic field and works best for certain tasks. The most common shapes include:
Cylindrical (disc or rod)
Square or rectangular (block)
Ring
Arc or segment
Sphere
Shape matters because it changes how the magnetic field spreads out. For example, a cylindrical magnet has its strongest field along the axis, while a ring magnet focuses the field inside and outside the ring. Square magnets show strong fields at the center but weaker ones at the edges. You should always match the magnet’s shape to your application’s needs.
Here is a table that compares how different shapes affect magnetic field distribution and performance:
Magnet Shape | Magnetic Field Characteristics | Effect of Size and Shape on Field Distribution and Strength | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
Cylindrical | Axial symmetry; strongest field along axis; radial component present; magnetic lines concentric around axis | Size and shape influence field strength and uniformity; field strength decreases with distance from the axis | Used in motors (rotors/stators) and sensors for controlled magnetic fields |
Square | Complex distribution; stronger field at center, weaker at edges; strong directional variation | Size and shape cause non-uniform field strength and directional differences | Used in magnetic materials research and magnetic separation technology |
Ring | Magnetic field concentrated inside and outside the ring; weaker on the sides; magnetic lines form closed rings | Shape causes unique field concentration patterns; size affects field strength inside/outside the ring | Used in transformers and wireless charging for controlled magnetic fields |
Tip: The right shape helps you get the most out of your magnet by focusing the magnetic field where you need it.
Fit for Application
You need to choose a magnet that fits your equipment and delivers the right performance. Start by looking at your design. Ask yourself where the magnet will go and what it must do. For example, if you need a magnet for a motor, a cylindrical or arc shape often works best. If you want to hold or lift flat objects, a block or disc magnet may be the right choice.
Shape also affects how easy it is to install the magnet. Some shapes fit into tight spaces or curved surfaces better than others. Always check the available space and the direction you need the magnetic force.
Scientific measurements show that magnet size and shape can change the accuracy and uniformity of the magnetic field. Complex shapes may create uneven fields, which can make it harder to measure or control the magnet’s strength. Advanced tools, like 3D magnetic field cameras, help engineers map these fields and choose the best magnet for each job.
Note: If your application needs a very uniform or focused field, pay close attention to both the shape and the size of the magnet.
Sizing
Selecting the right size is just as important as picking the right shape. The size of a magnet controls how strong it is and how far its field reaches. Larger magnets usually have stronger fields, but they may not fit in small spaces. Smaller magnets can work if you use a higher grade or combine several units.
Follow these steps to choose the right size:
Measure the space where you will place the magnet.
Decide how much pull force or holding power you need.
Check if you need a thin or thick magnet for your design.
Consider whether you need to stack magnets or use them side by side.
Alert: A magnet that is too large may interfere with other parts. One that is too small may not provide enough strength.
By matching the size and shape to your application, you ensure the magnet works safely and efficiently. Always test your choice in real-world conditions before making a final decision.
Coatings and Protection
When you choose industrial neodymium magnets, you must think about how to protect them from corrosion and wear. Coatings play a key role in keeping magnets strong and reliable, especially in harsh or outdoor environments. Without the right coating, moisture, chemicals, and temperature changes can damage your magnets and shorten their lifespan.
Coating Types
You have several coating options for neodymium magnets. Each type offers different levels of protection and suits specific industrial needs. The table below compares common coatings and their main features:
Coating Type | Corrosion Protection | Wear Protection / Other Properties | Typical Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
Nickel-Copper-Nickel | Excellent, triple-layer | Durable, shiny finish | Motors, sensors, jewelry |
Zinc | Good, cost-effective | Simple, passivated layer | Automotive, switches, general industry |
Epoxy | Exceptional moisture/chemical | Abrasion-resistant, tough polymer | Outdoor, marine, wind turbines |
PTFE (Teflon) | High chemical resistance | Non-stick, easy to clean | Medical, food processing |
Gold | Excellent, tarnish-resistant | Thin, attractive finish | Electronics, medical devices |
Rubber | Shock absorption, waterproof | Non-slip, chip-resistant | Tools, toys, magnetic mounts |
Tip: Choose a coating that matches your environment and application. For example, use epoxy for outdoor or marine settings, and nickel for general industrial use.
Recent research from Hangzhou Dianzi University introduced a new “slippery liquid-infused porous surface” (SLIPS) coating. This advanced coating protects neodymium magnets from corrosion and wear better than standard coatings like nickel or epoxy. It works well against moisture, salt spray, and temperature swings, helping magnets last longer in tough conditions.
Environmental Resistance
You need to match the coating to the environment where you will use the magnet. Moisture, chemicals, and temperature changes can break down coatings over time. Studies show that coatings like epoxy and PTFE resist water and chemicals very well, making them ideal for humid or corrosive settings. Nickel and zinc coatings work best in dry or mild environments.
Note: If your magnets face saltwater, chemicals, or rapid temperature changes, pick a coating with high resistance. This prevents rust, pitting, and loss of strength.
Durability
Durability means how long the coating can protect your magnet under real-world stress. Research shows that coatings can lose strength from UV light, freeze-thaw cycles, and chemical exposure. For example, studies on polyurea and bitumen coatings found that moisture and temperature swings cause cracks and wear over time. Thicker coatings often last longer, but the right material matters most.
You should always check the coating’s thickness and quality. Test magnets in your actual environment if possible. If you expect heavy use or harsh conditions, invest in advanced coatings like SLIPS or thick epoxy.
Alert: Damaged or worn coatings expose the magnet to corrosion. Replace magnets or reapply coatings if you see chips, cracks, or rust.
By choosing the right coating, you protect your investment and keep your magnets working safely and efficiently.
Safety and Handling
Handling Tips
Industrial neodymium magnets have strong magnetic fields. You must handle them with care to prevent injuries and damage. Always use both hands when moving large magnets. Wear gloves to protect your skin from pinches or cuts. Eye protection helps shield your eyes from flying chips if magnets snap together.
Keep your fingers away from the space between two magnets.
Move magnets slowly and never let them slam together.
Use non-magnetic tools, such as plastic or wood, to separate magnets.
Place magnets on a flat, stable surface when not in use.
Alert: Neodymium magnets can shatter if they collide. Broken pieces can become sharp and dangerous.
You should also keep magnets away from electronic devices. Strong magnetic fields can erase data on hard drives, credit cards, or other storage media. Keep magnets at least several feet away from sensitive equipment.
Storage
Proper storage keeps your magnets safe and maintains their strength. Store magnets in a dry, cool place. Moisture can cause corrosion, even with protective coatings. Use original packaging or place magnets in padded containers to prevent chipping.
Stack magnets with spacers between them to make separation easier.
Label storage boxes with warning signs, such as “Strong Magnet—Handle with Care.”
Keep magnets away from metal tools and other magnets to avoid accidental attraction.
Store magnets out of reach of children and untrained staff.
Storage Tip | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
Use spacers or dividers | Prevents magnets from snapping together |
Dry, cool environment | Reduces the risk of corrosion |
Padded containers | Protects from chips and cracks |
Clear labeling | Warns others about magnetic hazards |
Tip: If you store magnets for a long time, check them regularly for signs of rust or damage.
Compliance
You must follow safety rules and regulations when using industrial neodymium magnets. Many industries have guidelines for handling and transporting strong magnets. Check local, state, and federal laws before shipping magnets, especially by air. Airlines often restrict large or unshielded magnets because they can interfere with navigation equipment.
Review OSHA guidelines for workplace magnet safety.
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for installation and disposal.
Use proper documentation when shipping magnets internationally.
Note: Some countries require special packaging or labeling for magnetic materials. Always check with your supplier or shipping company before sending magnets abroad.
By following these safety and handling tips, you protect yourself, your team, and your equipment. Safe practices help you get the best performance from your industrial neodymium magnets.
Testing and Expert Help
Prototyping
You should always start with prototyping before making a final decision on industrial neodymium magnets. Prototyping lets you test how the magnet works in your real application. You can check if the magnet fits, holds the right weight, and performs as expected. This step helps you avoid costly mistakes.
Build a small-scale model or use sample magnets.
Test the magnet in the actual environment.
Observe how it reacts to temperature, moisture, and vibration.
Tip: Prototyping can reveal problems that you might not see on paper. For example, a magnet may lose strength if it gets too hot or if the surface is not flat. You can adjust your design early and save time and money
Quality Checks
You need to make sure that every magnet meets strict quality standards. Quality checks help you avoid failures and keep your equipment running safely. Reliable suppliers will provide magnets that pass industry tests for strength, coating, and durability.
Here are some key quality checks to consider:
Quality Check | What It Confirms |
|---|---|
Pull Force Testing | Magnet meets the required holding strength |
Coating Inspection | Surface is smooth, no chips or cracks |
Dimensional Check | Magnet matches the specified size and shape |
Temperature Testing | Magnet keeps its strength at high/low temperatures |
You should ask for certificates or test reports from your supplier. Look for ISO 9001 or similar certifications. These show that the manufacturer follows strict quality control processes.
Alert: Never skip quality checks. Even a small defect can cause big problems in industrial settings.
Supplier Consultation
Consulting with expert suppliers gives you a major advantage. Experienced suppliers understand the technical details of neodymium magnets. They can help you choose the right grade, size, and coating for your needs. You also get advice on installation, safety, and compliance.
A real-world example shows the value of expert consultation. A 300+ bed hospital worked with HealthLinx consultants to achieve Magnet® Initial Designation. The hospital earned 9 Exemplars and gained a financial benefit of $850,000. The consultants’ deep knowledge and leadership helped the hospital improve patient safety, nursing engagement, and overall performance. This case proves that working with experts can lead to better results and significant savings.
Note: Expert suppliers often guarantee success and provide ongoing support. They can help you solve problems quickly and avoid costly errors.
You should always verify that your supplier has the right certifications and a strong track record. Ask about their experience with similar projects. Good suppliers will share references and proof of past success.
By following these steps—prototyping, quality checks, and expert consultation—you make sure your industrial neodymium magnets deliver safe, reliable, and cost-effective performance.
You can choose the right industrial neodymium magnets by following a few simple steps. First, define your application needs. Next, match the magnet’s grade, size, and coating to your environment. Always test your choice before final use. For complex projects, talk to a trusted supplier or expert. Review your requirements and take action to ensure safe and reliable results.
FAQ
What is the difference between neodymium magnet grades like N35 and N52?
Grades show the magnet’s strength. N52 is stronger than N35. You get more holding power from a higher grade. Choose a grade that matches your application’s force and size needs.
Can neodymium magnets lose their magnetism over time?
Yes, they can lose strength if exposed to high heat, strong impacts, or corrosion. Store and use them within recommended limits. Proper coatings and careful handling help keep magnets strong.
Are neodymium magnets safe to use around electronics?
No, strong neodymium magnets can damage electronics and erase data. Keep them away from computers, credit cards, and other sensitive devices. Use caution when working near electronic equipment.
How do I choose the right coating for my magnet?
Match the coating to your environment. Use nickel for dry areas, epoxy for wet or outdoor use, and PTFE for chemical resistance. The right coating protects against rust and wear.
Can I cut or drill a neodymium magnet to fit my project?
You should not cut or drill neodymium magnets. They can break, chip, or release harmful dust. Order magnets in the size and shape you need from the supplier.
What should I do if my magnet gets damaged or rusty?
Replace damaged or rusty magnets right away. Damaged coatings expose the magnet to corrosion and reduce its strength. Inspect magnets regularly and use proper storage to prevent future issues.
Do I need special shipping for industrial neodymium magnets?
Yes, you need special packaging and labeling for shipping strong magnets. Airlines and carriers have rules for magnetic materials. Check regulations before shipping to avoid delays or fines.


