Mounting magnets fail when chosen incorrectly. Loose fixtures can damage property, reduce efficiency, and waste money. The right mounting magnets secure loads safely by considering weight, surface material, and environmental conditions.
This guide explains everything you need to know about choosing, using, and improving mounting magnets for both DIY projects and industrial applications.
Table of Contents
What is a Mounting Magnet?
A mounting magnet is a specially designed magnet used to hold, fix, or attach objects to different surfaces. Unlike regular magnets, mounting magnets are optimized with protective coatings, housings, or holes for secure installation.
- Common uses: tool holders, signage, fixtures, vehicle accessories, and machinery mounts.
- Popular material: neodymium magnets (N35–N52) due to their high strength in compact sizes.
- Protective coatings: nickel or epoxy for corrosion resistance.
⚠️ Mistake to avoid: Choosing a magnet that’s too weak can cause dangerous slippage, while an overly strong one can damage surfaces or be difficult to remove.
What Are the Different Types of Mounting Magnets?
Different projects require different types of mounting magnets. Below are the most common categories:
| Type | Main Feature | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Pot Magnet | Steel shell enhances pull force | Industrial mounting, machinery |
| Channel Magnet | Slim design with elongated pull | Shelving, signage |
| Rubber-Coated Magnet | Surface protection + weather resistance | Vehicle mounts, outdoor use |
| Hook/Eyebolt Magnet | Hanging capability | Temporary installations, lighting |
| Disc Magnet | Compact + strong | Fixtures, electronic mounts |
| Block Magnet | Very high force | Heavy-duty industrial setups |
👉 Pro Tip: Many pot and channel magnets actually use neodymium disc magnets inside to maximize holding power.
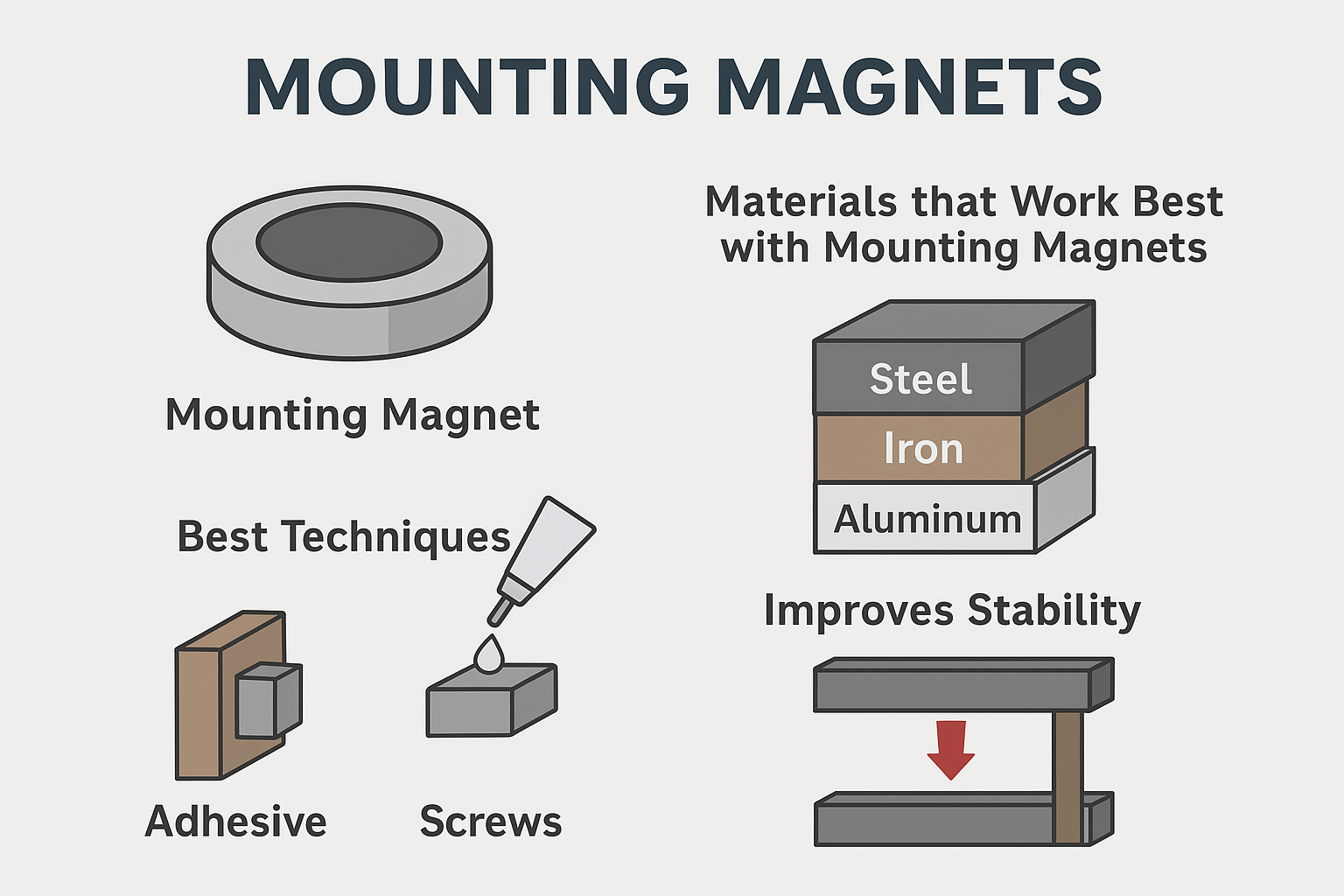
What Materials Work Best with Mounting Magnets?
Magnet performance largely depends on the surface material.
| Material | Magnet Compatibility | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel | Excellent | Maximum holding power |
| Iron | Good | Stable grip |
| Stainless Steel (304) | Poor | Non-magnetic |
| Aluminum | None | Not magnetic |
| Painted/Coated Steel | Reduced | Depends on thickness & coating |
✅ Best results come from clean, flat, and ferromagnetic surfaces (e.g., thick steel).
⚠️ Weak results happen with thin sheets, paint, rust, or gaps.
What Factors Determine Magnet Mounting Strength?
The holding force of mounting magnets is influenced by:
- Magnet grade (N35–N55) – higher grades mean stronger pull.
- Contact surface area – more surface = stronger hold.
- Base material thickness – thicker steel improves flux.
- Environmental conditions – moisture and heat can weaken magnets.
- Force direction – magnets are stronger in direct pull than in shear force.
📊 Example Test Data (50mm N52 disc magnet):
| Steel Thickness | Holding Power | Flux Completion |
|---|---|---|
| 2mm | 20kg | 35% |
| 5mm | 65kg | 72% |
| 10mm | 120kg | 98% |
Best Techniques for Mounting Magnets
There are three main techniques for securing magnets:
- Adhesive-Backed Magnets
- Easy to apply, good for light-duty tasks.
- Weak in humid/outdoor environments.
- Gluing Magnets (Epoxy, Super Glue)
- Strong permanent bond.
- Requires clean prep and curing time.
- Mechanical Fastening (Screws, Countersunk Holes)
- Strongest and most reliable.
- Ideal for industrial or heavy-duty use.
👉 Combine adhesive and mechanical fastening for maximum stability.
How to Attach Mounting Magnets to Wood
Step-by-Step Process:
- Drill a recess slightly deeper than the magnet.
- Clean both surfaces (magnet + wood).
- Roughen the magnet surface for better adhesion.
- Use epoxy or super glue.
- Let adhesive cure completely.
- Test the bond before use.
📌 Alternative: Use magnets with countersunk holes and screw them into wood for adjustability.
How to Improve Magnet Mounting Stability
Even strong magnets can fail if poorly installed. Here’s how to improve stability:
- Use higher-grade magnets (N52) for maximum force.
- Ensure clean, flat surfaces free of rust, paint, or dust.
- Recess magnets into surfaces to prevent sliding.
- Combine magnets with screws or bolts for vibration-heavy environments.
- Choose proper coatings (nickel for indoors, epoxy for outdoors).
📊 Factors Affecting Stability
| Factor | Impact | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Surface cleanliness | Weak hold | Degrease + sand surface |
| Magnet strength | Slippage | Upgrade to N52 |
| Shear force | Sliding | Add screws/countersunk |
| Environment | Corrosion, heat damage | Use epoxy-coated magnets |
Conclusion
Mounting magnets are essential for both DIY and industrial applications. The right choice depends on pull force, surface material, and environment.
Disc, block, pot, and channel magnets offer different benefits.
Neodymium magnets provide maximum strength in compact sizes.
Proper installation techniques (gluing, fastening, recessing) ensure stability.
Choosing high-quality mounting magnets prevents failures, saves costs, and improves safety.
👉 Explore related guides on neodymium magnets and magnetic mounting solutions to optimize your projects.


